Ⅰ. Challenges
Natural disasters are among major threats to agriculture globally. For many years, climate change has had a serious impact on agriculture, and farmers need to face severe challenges such as increased crop diseases and pests, climate warming, and frequent occurrence of extreme weather events.
According to the Emergency Events Database (EM-DAT) maintained by the Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters (CRED), which records disasters which have killed ten or more people; affected 100 or more people; resulted in a declared state of emergency, or a call for international assistance, in the period 2000 to 2019, there were 7,348 major recorded disaster events claiming 1.23 million lives, affecting 4.2 billion people (many on more than one occasion) resulting in approximately US$2.97 trillion in global economic losses.
In 2010, the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations pointed out in a report that developing countries need to develop "climate smart" agriculture to cope with the warming world and feed an increasing population.
Ⅱ. Solutions
Specifying basic evaluation units such as township or county, according to the type, scope, and severity of disasterand integrating multipletechnologies in the assessment contribute to effective and efficient post disaster reconstruction.
Major disaster loss Assessment includes:
● Physical Quantity Assessment
Incorporate various methods such as on-the-spot investigations, empirical models, Local statistics reports, and remote sensing interpretation. in the assessment of the physical quantities of damages and losses such as casualties, house damages and ruins, agricultural losses, industrial losses, losses in the service sector, losses in infrastructures, losses in social undertakings, residents’ property losses, and losses of Land resources.

Physical damages caused by floods
● Direct Economic Loss Assessment
Based on the physical quantity assessment, utilize multiple methods such as accounting to assess the direct economic losses caused to houses, agriculture, industries, the service sector, infrastructures, social undertakings, residents’ properties, and land resources.
● Disaster Scope Assessment
Take each assessment unit as the basic unit and assess a disaster’s intensity and distribution across a certain area.
Ⅲ. Measures:
● On-the-spot investigation and Assessment
After a disaster, on-the-spot investigation and assessment groups should be Established with membership from relevant professional departments and experts to carry out investigations.
The investigations are mainly conducted in the following aspects:
1) House damages and ruins
2) Agricultural losses
3) Losses in industry and the service sector
4) Infrastructural losses (in fields such as transport facilities, municipal facilities, water conservation facilities, power facilities, telecommunications facilities, radio and communication facilities, and governmental facilities.).
Data and devices required in the investigations mainly include:
1) On-the-spot questionnaires
2) Personal Digital Assistant (PDA) terminals
3) High-definition remote-sensing images of key areas, working layers of different regions gained from on-the-spot collection, and relevant thematic data.

On-the-spot investigation processes
● Remote sensing and monitoring of disasters
Take high-resolution data of key areas collected by aviation and unmanned aircrafts as the main source for investigation and incorporate ground investigation data in the monitoring and assessment of damages and losses caused to houses, infrastructures (especially transportation lines), and agricultural land such as croplands and woodland in the disaster-stricken areas.
● Local statistics reporting
According to the features of catastrophic disasters, design statistical indicators and formulate relevant files such as “Statistics Table of Disaster Losses” and the corresponding instructions on how to fill these statistics tables. Governments in disaster-stricken areas should organize and carry out an overall on-the-spot investigation, conduct statistical calculations and submit the results to the higher governments.
● Economic methods
On the basis of physical quantity loss assessment, integrate the disaster loss data reported by local governments with those from investigations and inspections of relevant departments and organizations; make calculations through the unit replacement cost for individual disaster-affected entities such as those entities in the form of houses, entities in industry, agriculture and the service sector, entities in infrastructures, entities in social undertakings, entities in the form of residents, properties and land resources.
● Disaster Scope Assessment --- Indicator Assessment Method
Take the assessment unit as the basic unit and select key indicators to construct comprehensive disaster indices. Divide a disaster-stricken area according to the varying intensities of a disaster in the area, with the help of the comprehensive disaster indicators.
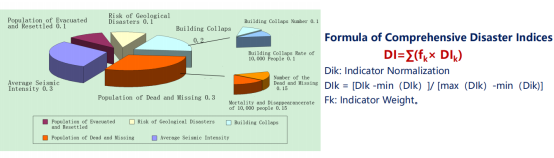
Disaster scope assessmentmodle
(Source:Workshop on Flood Response and Recovery – Henan Case)
Ⅳ. Application and outcomes
From July 17 to 23, 2021, central China’s Henan Province was hit by rare rains in history, resulting in serious floods. The disaster affected 14.786 million people in 150 counties (cities and districts) in the province, with 398 people dead or missing.
After the rainstorm, Henanconstructed a multidirectional assessment system:

Components of the assessment system
The Henan Flood Control and Drought Relief Headquarters proposed suggestions like downgrade of early warning or termination of emergency response activities, post disaster recovery and reconstruction, and disaster relief, according to prompt consultations and judgments. Relevant departments also conducted disaster assessment and post disaster recovery in their respective areas based on respective situations.
As of the end of March 2023, a total of 19,556 post disaster reconstruction projects have been completed, with a completion rate of 98.4%.
Sources:
The article is excerpted from Workshop on Flood Response and Recovery – Henan Case by Nie Juan
Category
Major Disasters Loss Assessment Based on Integration of Multiple Technologies
Contributor
Major Disasters Loss Assessment Based on Integration of Multiple Technologies
Country
Technical Solution

