
Advanced technologies in grain drying, storage, transportation, and processing have dramatically reduced post-harvest grain losses in China. Yao Lei, Director of the Science and Technology Division at the Department of Safe Storage and Science & Technology within China’s National Food and Strategic Reserve Administration, provides key insights into the outcomes, strategies, and lessons learned from China’s innovation-driven approach to post-harvest grain conservation — spanning the critical stages of procurement, storage, transportation, and processing.
1. Notable Achievements in Post-harvest Grain Conservation and Loss Reduction
1.1 Enhancing post-harvest services in grain procurement
Since 2017, China has established over 5,500 specialized post-harvest grain service centers, achieving full coverage across major grain-producing counties. These centers provide timely services such as grain drying and cleaning for farmers, effectively helping them reduce losses and improve quality and efficiency. Nearly 10 million sets of scientifically designed grain storage equipment have been promoted nationwide, reducing household grain storage losses from 8% a decade ago to 2.9%. Currently, technical guidelines for household grain storage and equipment selection are under development, aiming to provide more scientific guidance for farmers.

1.2 Advancing green storage technologies
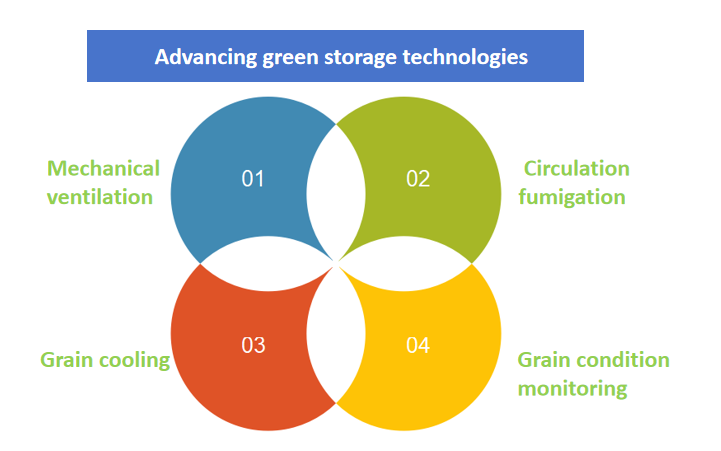
1.2.1 Integrated "four-in-one" systems
Grain storage facilities have widely adopted integrated "four-in-one" systems that combine mechanical ventilation, grain cooling, circulation fumigation, and grain condition monitoring. This technology effectively improves the internal storage environment of grain warehouses, reduces the risk of overheating that can occur in parts of the grain piles, and is now considered standard equipment in state-owned grain depots.
1.2.2 Controlled atmosphere storage technologies
Controlled atmosphere storage technologies using nitrogen, carbon dioxide, and other gases have proven effective in pest control and in slowing down grain quality deterioration. National data shows that facilities employing controlled atmosphere technologies now have a combined capacity of 55 million metric tons.
1.2.3 Temperature control technologies
Temperature control technologies commonly used in grain storage include non-refrigerated cooling, air conditioning, and internal air circulation systems. The application of temperature control technologies is gradually expanding, with low-temperature and near-low-temperature storage technologies playing a vital role in preserving grain quality and reducing losses.
1.2.4 Other new technologies
Since the launch of the 13th Five-Year Plan, the national key research and development program of China has implemented several grain storage research and innovation projects, such as the "Modern Grain Warehouse Green Storage Technology Demonstration Project." These projects have driven significant breakthroughs in critical grain preservation technologies, such as pest control, mold prevention, and loss reduction. By implementing these new technologies and standardized grain storage management practices, state-owned grain reserve enterprises have successfully kept their comprehensive losses below 1% during the storage period.
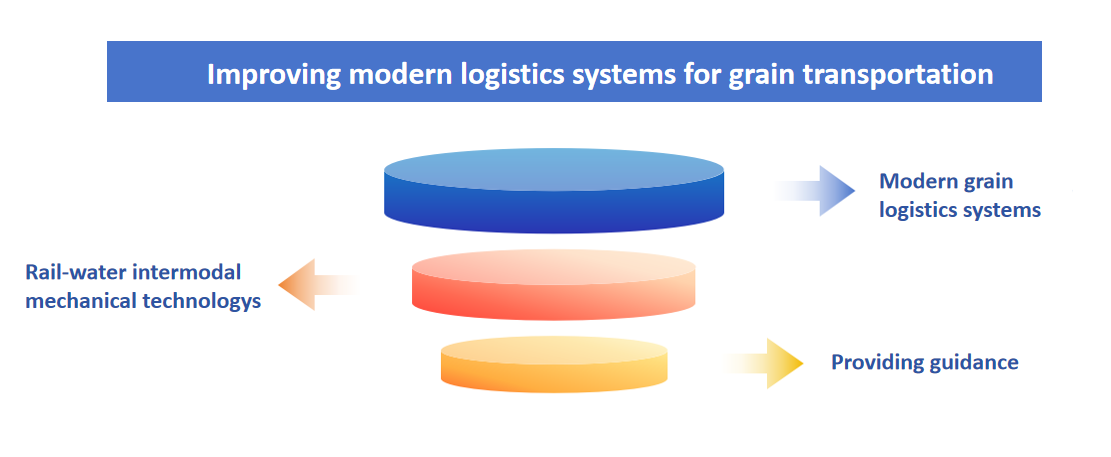
1.3 Improving modern logistics systems for grain transportation
The improvement of modern grain logistics systems plays a crucial role in minimizing losses during transportation. The adoption of rail-water intermodal mechanical technology, specialized railway carriages and bulk grain vehicles, and loading/unloading platforms has effectively reduced spillage, breakage, moisture, mold, contamination, and other losses during transportation. The National Food and Strategic Reserves Administration, together with the Ministry of Transport, National Railway Administration, China State Railway Group Co., Ltd., and other relevant bodies jointly issued the Technical Guidelines for Grain Transportation, providing guidance for the application of these technologies and equipment.
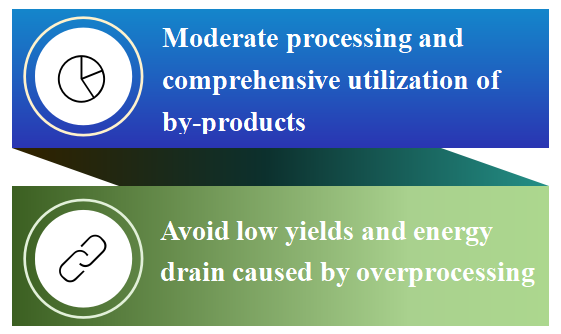
1.4 Advocating moderate processing concepts and comprehensive utilization of by-products
China’s National Food and Strategic Reserve Administration (the Administration) advocates for moderate processing of grain and comprehensive utilization of by-products. It develops and champions moderate processing technologies for ready-to-sell grain and oil products to avoid low yields and energy drain caused by overprocessing. Concurrently, it is drafting processing standards to define and avoid unreasonable processing precision, limiting unnecessary grain loss and curbing extra power consumption.
For example, the adoption of flexible rice milling equipment -- a new design that minimizes kernel breakage rate, frictional heat buildup, and power draw -- can increase white rice yield by 5 to 8 percentage points. Meanwhile, by maximizing the value of by-products like rice bran, wheat bran, and soybean meal, the administration improves overall grain utilization efficiency, which opens new avenues for grain conservation.

Rice processing
1.5 Enhancing consumer awareness and promoting behavior change
The Administration strengthens scientific education and promotes healthy consumption practices by championing grain conservation and discouraging waste. Through annual events such as World Food Day, National Grain Security Publicity Week, and National Grain and Material Reserve Science and Technology Week, the administration distributes promotional materials, hosts expert lectures, and rolls out online and offline activities. These efforts aim to convey the values of gratitude for grain, frugality, and healthy eating, creating a culture in which saving grain is a source of pride and wasting grain is shameful.
Meanwhile, the Administration pioneers innovative outreach strategies that bring grain and oil science education directly into communities, households, and schools, fostering scientific understanding, responsible consumption habits, and support for the "Clean Plate" campaign.
2. Leveraging Scientific and Technological Support for Grain Conservation and Loss Reduction
2.1 Strengthening institutional frameworks
To institutionalize grain conservation, China has issued relevant policy documents, laws, regulations, and plans, elevating the reduction of food loss and waste to a pillar of national food security and a core element of its spiritual civilization. It has enacted and put into force the "Anti-Food Waste Law of the People's Republic of China" and the "Grain Security Guarantee Law of the People's Republic of China," and has updated the "Regulation on the Administration of Grain Circulation." These legal instruments mandate innovation in preservation technologies, the application of proven conservation practices, and the prescription of specific conservation measures. China also embeds grain saving targets into the "Land Protection and Grain Security Responsibility Assessment."
2.2 Improving standards and specifications
Standards are essential to reducing grain loss throughout the supply chain. China has issued technical standards for grain covering storage, transportation, processing, and other sectors. For example, it has revised and issued conservation standards for rice and wheat flour. Next steps will focus on developing and revising standards related to green grain storage, launching pilot projects, and continuously promoting grain loss reduction through the guidance of standards.

Grain harvesting
2.3 Supporting technological innovation
To promote grain conservation and loss reduction, the National Engineering Research Center of Grain Storage and Logistics and other three national engineering research centers focusing on post-harvest loss management, along with 35 grain industry technology innovation centers (including engineering technology research centers), have been established, building a framework for post-harvest loss reduction technology innovation.
Food-grade inert powder, temperature control, controlled atmosphere, and other physical prevention and control technologies developed by grain research institutions are being actively promoted and applied. Biological and physical pest control technologies such as light traps, biological pest control using predatory mites and other natural enemies, spinosad, S-Methoprene, and plant-derived insecticides are being demonstrated and applied to control pests in stored grains.
However, post-harvest grain loss and waste still exist to varying degrees at various stages. Continued success will depend on raising awareness of loss reduction across the entire value chain and expanding the development and deployment of technological innovations.

Grain storage
3. Future Plans and International Cooperation
Throughout the 14th Five-Year Plan period, the National Food and Strategic Reserves Administration will further promote the implementation of its "Grain Conservation Action Plan" by:
• Promoting green grain storage and other technologies
• Enhancing digital oversight and leading development through standardization
• Promoting moderate processing
• Implementing integrated post-harvest grain conservation measures
• Demonstrating integrated grain conservation technologies
• Strengthening public education on gratitude for grains, their conservation, and healthy consumption
• Promoting international cooperation in grain science and technology
• Exchanging and sharing Chinese experiences
Reference:
The Expert Talk video series produced by the National Food and Strategic Reserves Administration of China
Innovation-driven Approaches to Post-harvest Grain Conservation and Loss Reduction
Related Links:
1. Corn Storage Equipment Types and Applicability
3. Corn Storage in Open-air Structures: Common Methods, Technical Requirements, and Considerations
4. Standards for Grain Conservation and Loss Reduction Across Different Circulation Stages
5. Wheat Mold Prevention, Control, and Loss Reduction Techniques
6. Ensuring Quality and Reducing Losses: Rice Harvesting and Storage Techniques in China

Category
Technical Solution
Contributor
Innovation-driven Approaches to Post-harvest Grain Conservation and Loss Reduction
Country
Technical Solution

