
Effective and safe storage methods for corn play a crucial role for farmers. Proper ventilation, moisture control, and careful handling help prevent spoilage, mold, and pest infestation. Professor Zhang Dongdong from the School of Food and Strategic Reserves at Henan University of Technology introduces common methods for storing corn in open-to-air structures, their technical requirements, and key considerations for both ear and kernel storage.
When corns are freshly harvested, they typically have high moisture contents. Farmers usually choose to store the corn ears directly and then thresh them once the moisture content decreases or they dry out. Common methods for storing corn ears include stacking them in piles, placing them on racks, or storing them in elevated cribs.
1. Ear corn storage

1.1 Stacking in piles
• The floor of the storage room should be elevated by at least 20 cm to ensure proper ventilation.

• Corn ears should be placed with the bottoms facing outward and the tops facing inward.
• Piles should be about 1 meter high and 1.2 to 1.5 meters wide. If the moisture content is higher than 30%, the width should be controlled within 1.2 meters, with a 20 cm ventilation gap between each pile.

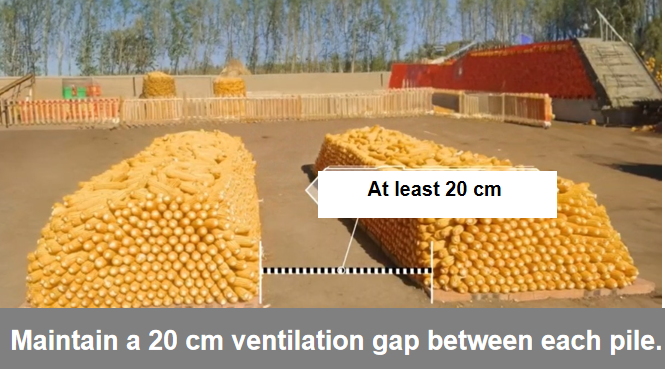
• Piles can be arranged in cuboid or cylindrical shapes.

Corn ears are placed with the bottoms facing outward and the tops facing inward.

Cylindrical stacking
1.2 Placing on racks
• Racks can be constructed using wood, steel wire mesh, or plastic netting to form cuboid structures that store corn ears inside.
• The width of the cuboids should be about 1.5 meters, and the height should not exceed 2 meters.
• The bottom should be elevated by at least 20 cm to ensure ventilation.

A cuboid corn storage rack
1.3 Storing in elevated cribs

Various types of elevated cribs are common storage forms for corn ears too.
• They can be made with steel pipes or wooden poles as the frame, and steel wire mesh, bamboo, or wood boards as the enclosure.
• Width: 1.5 to 2 meters.
• Height: 2 to 3 meters with wooden poles, 3 to 4 meters with steel pipes.
• Length depends on the available space.
• The cribs should be elevated at least 20 cm from the ground to ensure ventilation.
• For corn ears with moisture content below 28%, large steel-frame metal mesh silos with a capacity of 150 cubic meters can be used for natural ventilation and drying during winter and spring by taking advantage of low temperatures.
• If the moisture content is around 30%, a smaller 35-cubic-meter metal mesh steel-frame silo can be used for short-term storage.
Grain storage facilities should be placed in well-ventilated locations. If the storage is located in a courtyard, the direction of the facility should be perpendicular to the housing or at least 1.5 meters away from the house. The foundation should be flat and firm.

A wooden frame elevated crib (left), a steel frame elevated crib (right)

A large steel-frame metal mesh silo

A small metal mesh steel-frame silo
2. Corn kernel storage
When threshing corn, it’s crucial to follow the equipment operation guidelines to avoid excessive breakage of the kernels. After threshing, the corn can be cleaned using methods like air blowing and screening to remove dust, stones, damaged or shrivelled kernels, and pests. This ensures that only clean, full kernels are stored.

A worker uses a tool to lift the corn kernels, allowing the wind to remove impurities.

Left photo: a screening device used to remove impurities from corn kernels before operation.
Right photo: The machine in operation, a large quantity of yellow corn kernels covers the entire screen surface, while small stones and other impurities remain above, unable to pass through the holes.
• Warehouses should be moisture-proof, heat-insulating, insect-proof, rat-proof, airtight, and easy to maintain.

• Options include brick-and-concrete warehouses, prefabricated cement warehouses, single-story warehouses, or small steel structure warehouses.
• Cleanliness, drying, and pest control measures should be taken.
• If the temperature of the corn grains is high, it is best to cool them to room temperature before entering the warehouse.
• Try to choose times like sunset or nighttime when the temperature is lower, especially for dried corn to avoid high-temperature entry.


Regular checks should be conducted during storage to monitor the condition of the grain. Any issues should be addressed promptly to ensure safe storage. Farmers should choose the appropriate type of storage facility according to their specific conditions to preserve the corn and prevent mold growth or spoilage.
Reference:
The Expert Talk video series produced by the National Food and Strategic Reserves Administration of China
Corn Storage in Open-air Structures: Common Methods, Technical Requirements, and Considerations
Related Links:
1. Corn Storage Equipment Types and Applicability
3. Wheat Mold Prevention, Control, and Loss Reduction Techniques
4. Standards for Grain Conservation and Loss Reduction Across Different Circulation Stages
5. Innovation-driven Approaches to Post-harvest Grain Conservation and Loss Reduction
6. Ensuring Quality and Reducing Losses: Rice Harvesting and Storage Techniques in China

Category
Technical Solution
Contributor
Corn Storage in Open-air Structures
Country
Technical Solution

